I wrote this article to address common Google Penalties you may encounter as a website owner or as someone who helps clients fix Google Penalty Issues that may occur.

There are 2 main penalties website owners may encounter including a Manual Action penalty and an Algorithmic penalty.
Depending on the penalty and severity, a website’s traffic can nosedive in a single day and remain that way until the penalty or penalty issues are resolved.
Google Penalty History
Throughout the years Google has implemented Google algorithm updates to the chagrin of many website owners who haven’t adhered to SEO best practices and white hat techniques.
Many of the major Algorithmic updates were named after animals.
- Panda
- Pinguin
- Hummingbird
- Pigeon
- Maccabees
- Possum
- Rank Brain
- Mobile Speed
- Mobile 1st Indexing
1. Panda
RELEASE DATE: February 24, 2011
GOAL: Google’s goal is to lower the rank of websites that use duplicate content, plagiarized or thin content; user-generated spam; keyword stuffing.
NICKNAME: Farmer
ALGORITHM CHANGE: Panda assigns a ranking “quality score” to website pages, which is used as part of the overall ranking for the page. Duplicate content and thin content will lower the quality score making the page’s content much less likely to rank.
2. Penguin
RELEASE DATE: April 24, 2012
GOAL: Google’s goal is to lower the rank websites that use spammy or irrelevant links to content.
ALGORITHM CHANGE: Google uses real-time Penguin updates to scan for what it considers bad links and lower the quality score of pages and websites the links point to.
3. Hummingbird
RELEASE DATE: August 22, 2013
GOAL: Google’s goal is to improve search results based on User Intent and filter lower quality scores of websites that use keyword stuffing and low-quality content.
ALGORITHM CHANGE: Google has improved it’s searching algorithm by using natural language processing (NLP) which relies on latent semantic indexing, co-occurring terms and synonyms. Rather than just relying on keywords to return searches, Google tries to match the User Intent with the result set that gets returned.
4. Pigeon
RELEASE DATE: July 24, 2014 (US); December 22, 2014 (UK, Canada, Australia)
GOAL: Google’s goal with Pigeon is to focus on local ranking scores including both on an off-page SEO.
ALGORITHM CHANGE: Google focuses both on the local and traditional algorithms to calculate local ranking scores.
5. Mobile
RELEASE DATE: April 21, 2015
GOAL: Google’s goal with Mobile is to rank websites higher that have a mobile version and are mobile-friendly.
NICKNAME: Mobilegeddon
ALGORITHM CHANGE: Google’s Mobile Update focuses on rewarding websites with higher rankings that are mobile friendly and optimized for mobile.
6. RankBrain
RELEASE DATE: October 26, 2015
GOAL: Google’s goal with RankBrain (part of the Hummingbird algorithm) is again to try and optimize rankings based on user intent.
ALGORITHM CHANGE: Google implemented machine learning to try to calculate overall ranking scores for websites and content that best met user query intent.
7. Possum
RELEASE DATE: September 1, 2016
GOAL: Google’s goal with Possum is to create a more competitive ranking score based on location.
ALGORITHM CHANGE: Google implemented local ranking bonuses for results that are closer to the searcher location.
8. Fred
RELEASE DATE: March 8, 2017
GOAL: Google’s goal with Fred is to downgrade websites that use thin, affiliate-heavy or ad-centered content.
ALGORITHM CHANGE: Google implemented stricter enforcement of their Google webmaster guidelines pertaining to thin content and ad-centered content.
Google Manual Penalties
Unknown to many, Google is actively engaged in manual actions (i.e. manual Google Penalties) to the turn of 400,000 times a month. Beyond this, Google also introduces various algorithmic updates, including major ones like Penguin and Panda.
Google’s ultimate goal is to provide the best possible answers and content to user searches and user intent. Websites that through various techniques and tactics try to attract users that Google considers spammy or unethical (“Black Hat” SEO) and violated Google’s quality guidelines eventually get penalized.
Google Manual Penalty Issues | Why Am I Being Penalized?
Google Penalties can come in various forms, but the most common include.
- Link Schemes
- Thin Content | Scraped Content
- Keyword Stuffing
Link Schemes
Link Schemes (i.e. unnatural links) is one way Google will penalize a website. Many of these issues come up because a site owner has paid for backlinks from link farms or from Private Blog Networks (PBNs).
The goal of PBN’s and why they are often used is for the purpose of ranking higher in Google’s search engine. The theory is the more backlinks you have to your website, the higher it will rank, which in turn will generate more visits.
In many cases, Google can flag this type of activity as unnatural. For most websites, backlinks and link building happens naturally over time.
Outbound Links
Another issue that Google Checks, that is similar to inbound links are links going out from a site. Sometimes site owners use link exchanges to build authority exchanging links with other websites aren’t relevant to their content.
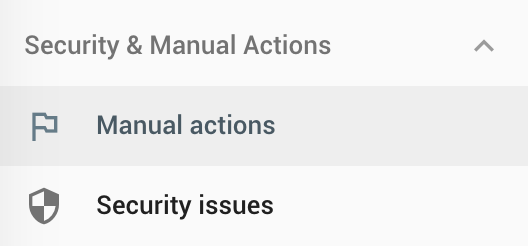
Manual Actions | Google Search Console
In Google Search Console, you can view messages from Google when your site has a manual action penalty applied to it.
To do so, open up Google Search Console and click on Security & Manual Actions –> Manual Actions
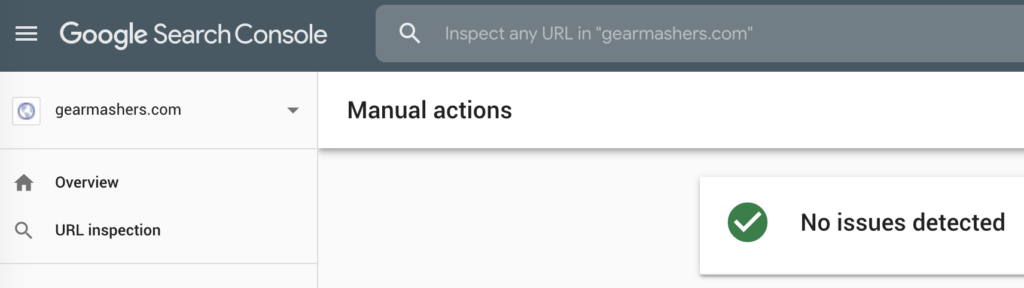
If a manual action is required, a message will display identifying the issue and what needs to be done to resolve the problem.
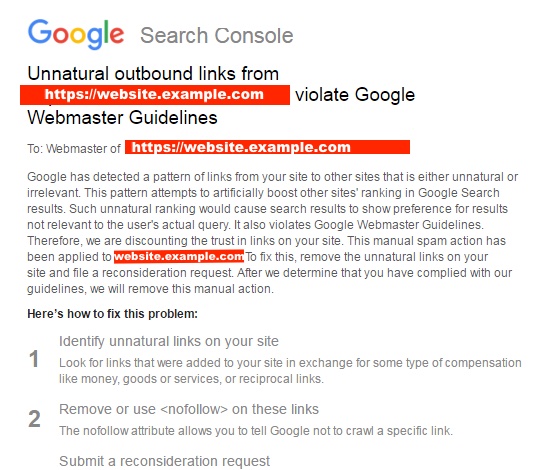
Thin Content | Scraped Content
Back in 2013, Google introduced a thin content manual penalty. At that time Google stated that thin content was against its Webmaster Guidelines.
So what is Thin Content? Google considers thin content to be any page where the majority of the content is of low-quality or shallow and doesn’t provide users with much added value. Doorway pages, automatically generated content or scraped content can trigger a manual penalty.
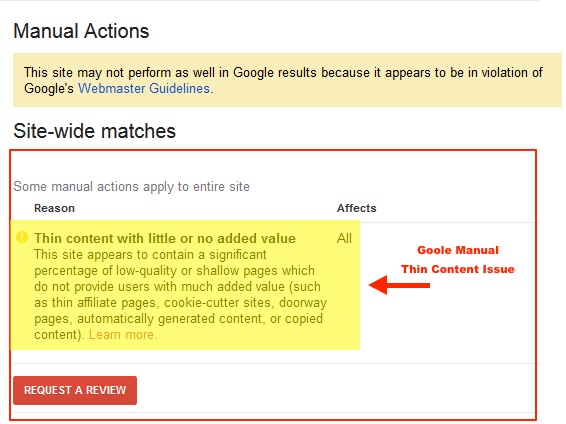
Like other manual actions, thin content can be fixed and will require a review request before the thin content penality is removed.
Types Of Thin Content
There are several types of thin content including
- Autogenerated content
- Doorway pages
- Scraped content
- Thin affiliate sites
As Matt Cutts explains through various examples of how websites might get flagged as having thin content and how to fix the problem.
Usually, there are 2 ways to fix thin content including issue including
- Rewriting flagged Thin Content pages with more in-depth unique content
- Remove/Delete Pages flagged with Thin Content
Keyword Stuffing
How Do I Recover?
Google knows that not all penalties are caused by unethical or deceitful practices, so they allow a website owner to rectify the situation and submit the offending links or website for review.
If your website has been subject to a manual penalty, the issue or issues will be listed in Google Search Console’s manual action section.
Other penalties like Panda or Penguin may be identified using Google Analytics.